USER GUIDE
INTRODUCTION
Hearing impairment and its prevalence in children :
According to the hearing report by the World Health Organization (2021), more than five percent of the global population, including 43.2 core adults and 3.4 core children, have a moderate degree of hearing loss. This number will increase to 70 core by 2050. It is important to note that a significant share of number is from the Western Pacific Region (13.65 Cores), followed by South-East Asia (10.94 Cores). Verme et al. (2021) reported the prevalence of hearing impairment in India. They found the prevalence of newborn babies was between 1.59 and 8.8 per 1000 births, whereas, in children, it was 6.6% to 16.47%. It is clear from these reports that early identification and early intervention of hearing impairment in children is crucial during their critical period for better speech and language development (Yoshinaga-Itano et al., 1998).
Cochlear implant and auditory training :
The cochlear implant is an electronic device to bypass the damaged part of the ear and directly stimulates the hearing nerve, helping the child to hear sounds. It has two parts; internal and external parts. The internal part is placed surgically inside the inner part of the ear. The external parts capture the sound and send it to the internal part. After the cochlear implantation surgery, the child hears the sound for the first time. It is a unique experience for the child and parents. After implantation, the child needs to undergo a listening or auditory training program to learn to listen through the cochlear implant device. The auditory training helps the child to develop speaking and understanding abilities. Experts recommend cochlear implantation at a younger age for improved speech and language outcomes (Ching et al., 2018).
Need for a comprehensive smartphone or computer-based application for auditory training :
The state of Tamil Nadu performs a total of 3000 cochlear implantation surgeries through government-based insurance schemes (Sampath Kumar & Kameswaran, 2018). The JIPMER hospital, located in Puducherry, performs 50 cochlear implant surgeries annually. These surgeries are through government-based insurance schemes. It shows the volume of surgeries done and the burden of sensorineural hearing impairment. After cochlear implantation, children need regular auditory training and speech-language therapy sessions. With the current shortages of Audiologists and Speech-language pathologists, there is a need for new and innovative ways of delivering therapy to children. In addition, cochlear implant surgeries are done only in major cities. Parents or caregivers from all over the country go to such cities to get their children operated on and attend therapy sessions. Most parents from resource constrained areas find it difficult to travel to the therapy centers and avail of the services. It is due to the distance from their domicile to the therapy center and its associated financial constraints. There is also a language barrier in availing therapy in a multilingual country such as India. There is also an increasing number of cases lost on follow-up due to these reasons. Considering the shortage of professionals for delivering therapy, the increasing number of children implanted, distance, and financial and language constraints, the need for developing a digital version of live therapy arises. The smartphone or computer-based application will supplement regular face-to-face therapy. It helps the parents train the child back home, thus improving their ability to listen and speak.
General overview of the smartphone or computer-based application :
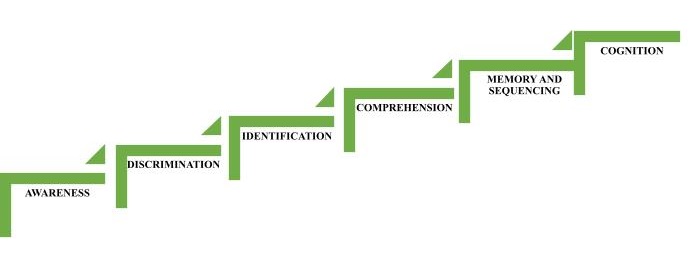
The stages of listening or auditory training are auditory awareness, discrimination, identification, comprehension, memory and sequencing, and auditory cognition, as shown in Figure 1 (Erber, 1982). The child starts the training from auditory awareness and moves on to the following levels till the last stage of auditory training, i.e., cognition. The following are three options common to each stage of auditory training except auditory awareness. The options are preview, training, and testing.
- Instructions for Preview
- Instructions for Training
- Instructions for Testing
Here, the child is introduced to the concepts. A few examples show the child how to perform the task in each listening/auditory training stage. This section may help the child to learn concepts. The child is not required to perform any task in this section. This section is, therefore, not scored
Here the child is given practice with the learned concepts. During the training, the child is asked to perform the task and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses. A thumbs-up symbol is for the correct response, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response. There is no scoring in this section.
After the training, to evaluate whether the child understands a particular concept, he/she undergoes testing with a scoring system. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response. After completing the testing, the child is provided with the total number of correct and incorrect scores so that the child undergoes additional training for the incorrect responses.
Stages of listening or auditory training
CATEGORIES
1. LING SIX SOUNDS
The Ling six sounds (ah, ee, oo, mm, ss, sh), as depicted in Figure 2, represent the speech range from low to high pitch or frequency. The ‘mm and oo’ represent low-pitched sounds, the ‘a’ represents the mid-pitched sound, and ‘ee’, ‘ss’, and ‘sh’ represent high-pitched sounds. To develop listening and speaking skills, the child needs to hear, listen and identify all these six ling sounds. Perform activities with the child where he/she has to indicate whether the ling sound is present or absent. The parents can train the child at home by using stacks of rings wherein they can keep the ring close to the ears, and whenever sound is present, the child has to keep the ring down. The child should not keep the rings down if there is no sound. In this way, the child is made aware of the sounds. Through this activity, the child will learn to listen and only place the ring down after he/she hears the sound. The ling six sound test helps the parents to ensure that the child can hear all the speech sounds since it covers the frequency range of speech before starting the therapy.
 Ah Ah |
 Ee Ee |
 Mm Mm |
 Oo Oo |
 Ss Ss |
 Ssh Ssh |
2. AUDITORY AWARENESS
(Presence or absence of sound)
Definition
Auditory awareness is the first step in auditory development. It means whether the child can detect the presence or absence of sound in their environment. After the cochlear implant is switched on, the child may respond to your voice or loud sounds in the background. The child may exhibit various kinds of responses to sounds. These responses include body movements (startle), smiling, head-turning or searching for the sound source, and eye movements/blinks. There can also be quieting responses (decrease in ongoing activity), increasing activity, starting or stopping crying, and changes in facial expression. Observe the childs reactions to various sounds in the environment, such as sounds for household items, vehicle sounds, animal cries, music, and meaningful speech sounds.
Task
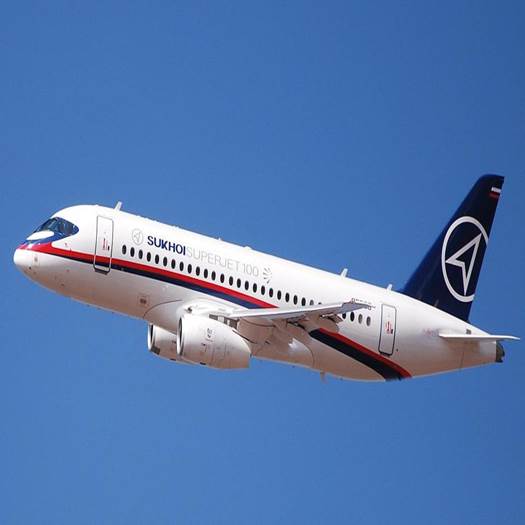
In the auditory awareness activities, your child has to indicate whether the sound is present or absent. The parents can train the child at home by alerting them, turning them towards the sound source, saying ‘Listen,’ and then naming the sound. Through this, the child understands that sounds have associations and meanings. For example, turn your child to the sound source with an aeroplane and label it. Say, "Listen, I can hear the sound of an aeroplane." It is up in the sky. Look at the aeroplane. Can you hear the sound of an aeroplane? It is an important strategy to develop the skill of localizing sound. In this way, the child is made aware of the sounds. There are two icons shown in the App or website based on whether the audio or sound is present or absent in the video. For example, if the child can hear the sound of the aeroplane, they can select the ’audible’ option. If the aeroplane sound is absent, the child can choose the ‘silent’ option on the screen. The parents can observe their responses for younger children and select on their behalf.
- Environmental Sounds
- Vehicle Sounds
- Animal Sounds
- Instrumental Sounds
- Learning to listen sounds
It includes a broad range of environmental sounds the child hears around them daily, such as door opening and fan noise.
It includes different types of vehicles and their associated sounds, such as ‘motorcycle’ and ‘helicopter.’
It includes animals such as ‘cat’ and ‘cow’ and their associated cries.
It includes musical instruments and their associated sound, such as ‘Guitar’ and ‘Violin.’
These sounds are easy to hear and associated with a particular object, adding meaning to the sounds and following normal language development. For example, associate the vehicle ‘bus’ with the sound ‘Buhbuh’ and the animal ‘cat’ with the sound ‘Meoww.’
2. AUDITORY DISCRIMINATION
(Difference of sounds)
Definition
It is the ability to tell the difference between sounds, i.e., whether they are the same or different. After the awareness stage, the child begins to understand the sound differences. This ability is called auditory discrimination. They will be able to understand the difference between loud and quiet sounds, high and low-pitched sounds, long and short sounds, and vowel and consonant sounds. Auditory discrimination plays an essential role in language and reading skills development.
Task
The parents must expose the child to two sounds that may be the same or different. The child has to listen to the pair of sounds and indicate whether both sounds are the same or different. Suppose the child cannot perform this task. In that case, the parents can move to the next category, "Auditory Identification."
- Instructions for Preview
- Instructions for Training
- Instructions for Testing
Here, the child is introduced to the concept of auditory discrimination. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept. For example, the words "Back" and "Back" are the same. Therefore, the pictures consist of two circles that appear in the same colour (blue) to represent that the sounds are the same. The words "Book" and "Took" are different from each other. Therefore, the pictures consist of two circles that appear in different colours (red and yellow) to represent different sounds.
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept. During the training, the child gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses. For example, when the audio of the words "Back" and "Back" is played, two choices with pictures are displayed. These choices represent identical sounds with the same coloured circles (blue) and different with different coloured circles (red and yellow). The child has to choose the picture with circles that are the same(blue) as the correct response. A thumbs-up symbol is for the correct answer, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect answer. There is no scoring in this section.
To evaluate whether the child understands the concept of auditory discrimination, they undergo testing with a scoring system. A score of 1 is for the correct answer, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer. For example, if the child chooses the pictures with the same coloured circles for the audio "Ball – Ball," then a score of 1 is given for this correct response. After completing the testing, the child is provided with the total number of correct and incorrect scores so that the child goes for additional training for the incorrect responses.
Auditory discrimination or difference of sounds - Category 3 in the App includes five categories. They are- Short and Long words
- High and Low-Frequency words or Words differing in pitch
- Minimal Pairs or Similar words
- Length of utterances (Monosyllable v/s syllable or trisyllable or multi-syllable words)
- Musical Instruments
There will be two words containing vowels that differ in duration. One vowel is of short duration, and the other vowel is of long duration. For example, the words "Sit" and "Seat" differ in the duration of the vowel, wherein one vowel is short duration as in "Sit." The other vowel is long duration, as in "Seat."
Here the child is trained to differentiate between high-frequency (high pitch) and low-frequency (low pitch) vowels and consonants
A. Words differing in pitch or frequency – consonants
The words contain high-pitched or high-frequency and low-pitched or low-frequency consonants. The low-pitched consonants are /p/, /b/, /m/, and /n/, and the high-pitched consonants are / t/, /d/, /f/, and /s/. The child must tell whether the words have the same or different consonants. For example, the words "Sauce" and "Nose" are different in consonant pitch, wherein one consonant is high pitch, as in "Sauce", and the other is low pitch, as in "Nose".
B. Words differing in pitch or frequency – vowels
The words contain high-pitched or high-frequency and low-pitched or low-frequency vowels. The high-pitched vowels are/i/, /I/, and /ɛ/, and the low-pitched vowels are / o/, /u /, and /U/. The child has to tell whether the words containing vowels are the same or different. For example, the words "Peel" and "Pool" are different in pitch, wherein one vowel is high pitch as in "Peel", and the other is low pitch as in "Pool".
These are pairs of words differing in one sound and have distinct meanings. The child learns to differentiate the pairs in terms of place, manner and voicing characteristics of the two sounds. For example, the sound /b/ in the word "bat" and the sound /k/ in the word "cat" differ in place, manner, and voicing characteristics. It consists of three levels.
A. Level 1
The pair of words differs in all three characteristics: place, manner, and voicing. For example, the sound /m/ in the word "mat" and the sound /f/ in the word "fat" differ in place, manner, and voicing characteristics.
B. Level 2
The pair of words differ in any two characteristics of the place, manner, and voicing. For example, the sound /m/ in the word "man" and the sound /p/ in the word "pan" differ in manner and voicing characteristics.
C. Level 3
The pair of words differs in one characteristic: place, manner, and voicing. For example, the sound /m/ in the word "mine" and the sound /n/ in the word "nine" differ only in place characteristics.
Monosyllable words are words with one syllable, such as "Car". Bisyllabic words are words with two syllables, such as "Car-rot". Trisyllabic words are words with three syllables, such as "ba-na-naa. Multi-syllable words are words with more than three syllables, such as "cau-li-flo-wer." The parent must present the child with words that differ in length, that is, short and long words. The child must listen to the words carefully and say whether they are the same or different.
A. Level 1
I. Monosyllable v/s polysyllable :
The child has to differentiate between monosyllable and polysyllable words. For example, "Car" and "he-li-cop-ter".
B. Level 2
II. Monosyllable v/s trisyllable :
The child has to differentiate between monosyllable and trisyllable words. For example, "Kite" and "Ba-na-naa.".
III. Bisyllable v/s polysyllable
The child has to differentiate between Bisyllable and polysyllable words. For example, "Sister" and "Su-per-mar-ket"
C. Level 3
IV. Monosyllable v/s bisyllable :
The child has to differentiate between Monosyllable v/s syllable words. For example, "Blue" and "Winter".
V. Bisyllable v/s trisyllable :
The child has to differentiate between Bisyllable v/s trisyllable words. For example, "Birth-day" and "Fam-i-ly".
VI. Trisyllable v/s polysyllable :
The child has to differentiate between Trisyllable v/s polysyllable words. For example, "Shop-keep-er" and "Pho-tog-ra-pher".
It includes different musical instruments that produce various musical notes, and the child has to differentiate whether they are the same or different. For example, "Flute" and "Guitar".
3. AUDITORY IDENTIFICATION
(Identifying words)
Definition
It is the ability to recognize spoken utterances. The child has to point, repeat or write what they have heard. The child attaches meaning to a sound by identifying what object is making the sound or attaches a word to a picture/object. When the parent says the word, the child has to listen and select the correct picture from an array of pictures. Here, the child should recognize the sound and source of the sound.
Task
The parents must expose the child to the words in the App with pictures. The child has to listen and recognize the word and choose the word among the images given. For example, the parent plays the word "Cat" and after listening to the word, the child has to select or point to the picture of a cat among other pictures.
- Instructions for Preview
- Instructions for Training
- Instructions for Testing
Here, the child is introduced to the concept of auditory identification. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept. For example, the word "Ankle" audio will be played and displayed in a picture
Here, the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses. In the training session, there are levels according to the number of choices offered. In the first level, there will be two choices. For example, for the audio with the word "Ears", two picture options, i.e., "Ears" and "Eye", are given. In the second level, there will be three choices. For example, for the audio with the word "Lips", three picture options, i.e., "Lips", "Feet", and "Nose", are given. After completing the first level, the child can move to the next level. The child has to carefully listen to the audio of the word and select or point it out among the two or three choices given. A thumbs-up symbol is for the correct response, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect answer. There is no scoring in this section
To evaluate whether the child understands the concept of auditory identification, they undergo testing with a scoring system. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer. For example, suppose the child chooses the picture "Ears" after listening to the audio "Ears", among other images. In that case, a score of 1 is for this correct response. After completing the testing, the child is provided with the total number of correct and incorrect scores so that the child goes for additional training for the incorrect responses
Auditory Identification or Identifying words - Category 4 in the App has 24 categories. It includes the following: body parts, fruits, animals and birds, vegetables, vehicles, action verbs, colors, trees and flowers, shapes, public places, occupation, food items, names of things in the house, gender, part of the day, clothing, emotions/feelings, festivals, national symbols of India, habits, identifying family members, identification of simple words differing in frequency characteristics, identification of minimal pairs which differ in the frequency characteristics of vowels, identification of pair of words which differ in the frequency characteristics of consonants, alphabets and numbers
4. AUDITORY COMPREHENSION
(Understanding speech)
Definition
It is listening and understanding spoken utterances such as sentences and conversations. Here the child can grasp the meaning of the spoken message. The child has to hear the phrase or sentence and understand and learn the meaning of the spoken message. The child has to perform the activity, answer the question, and choose the appropriate option for the questions asked. The child has to listen to stories, understand them and then answer the questions related to the story to know how well the child has understood the story.
Task
The parents must expose the Apps words or phrases to the child. The child must listen and understand the audio message and perform the activity or answer the questions. Auditory comprehension or Understanding speech - Category 5 in the App has four categories, with three levels in each category. It includes Commands, Yes/No questions, odd one out and Stories.
a. Commands :
Orders or commands are given for a child to follow. It has three levels. One-step commands in level 1, such as "Sit". Two-step commands in level 2, such as "Close the door". Three-step commands in level 3, such as "Take the pen and write".
- Instructions for Preview
- The word "Bend" audio will be played and displayed in a picture in level 1
- The phrase audio "Catch the ball is played and displayed in a picture in level 2
- The phrase audio "Point to your nose and mouth" is played and displayed in a picture in level 3
- Instructions for Training
- The word "Bend" audio will be played and displayed in a picture in level 1. The child must follow the command "Bend"—two choices, "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, a thumbs-up symbol is for the correct response, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete answer
- The audio for the phrase "Catch the ball is played and displayed in a picture in level 2. The child has to follow the command "Catch the ball"—two choices given as "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete response
- The phrase "Point to your nose and mouth" audio is played and displayed in a picture in level 3. The child must follow the command, "Point to your nose and mouth—two choices given as "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, a thumbs-up symbol is for the correct response, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete answer
- Instructions for Testing
- The word "Bend" audio is played in level 1. The child has to follow the command "Bend" two choices given as "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, they get a score of 1 for the correct response and 0 for the incorrect or incomplete response.
- The phrase "Catch the ball" audio is played in level 2. The child must follow the command "Catch the ball"—two choices are "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, a score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect or incomplete response.
- The audio for the phrase "Point to your nose and mouth" is played in level 3. The child must follow the command, "Point to your nose and mouth—two choices given as "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, a score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect or incomplete response.
Here the child is introduced to the concept of commands in auditory comprehension. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses. In the training session, there are levels according to the complexity of the task.
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of commands in auditory comprehension. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response
b. Yes/no questions :
Here the question is framed so that the child should understand it, think about it, and respond as "yes" or "no". For example, the parent asks the child, "Is ice cream cold?" The child must listen to the question and answer "yes ".
- Instructions for Preview
- The following question, "Is breakfast coming before lunch?" is played, and the answer is displayed as "yes".
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the question "Is breakfast coming before lunch?" is played. The child has to answer the question, and two choices are "Yes" and "No". Suppose the child correctly responds "Yes" to this question. In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response.
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the question "Is breakfast coming before lunch?" is played. The child must answer the question, and two choices, "Yes" and "No", are given. If the child correctly responds "Yes" to this question, then a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response
Here the child is introduced to the concept of yes/no questions in auditory comprehension. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of yes/no questions in auditory comprehension. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response
c. Odd one out :
It is the ability to recognize a word that is different in category from other words. The parent has to present four words to the child orally. The child has to listen and recognize the word that is different from the other three words. For example, the parent says, "Bicycle, Scooter, Auto, and Banana". Here "Bicycle, Scooter, Auto" belongs to the category of vehicles, whereas "Banana" is different as it belongs to the category of fruits. The child must listen to the words and find the word that is different (odd). The levels increase in complexity from levels 1 to 3. Gross differences between the categories are in level 1, such as "Bunch, desk, table, lotus". Moderate differences between categories are in level 2, such as "Milk, tea, coffee, noodles, and fine or minute differences between categories are in level 3, such as "Eyes, legs, ears, and nose.".
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the words "Bicycle, Scooter, Auto, Banana" is played and displayed in a picture in level 1. The odd one, "Banana", is highlighted
- The audio for the words "Apple, Watermelon, Grapes, Tomato" is played and displayed in a picture in level 2. The odd one, "Tomato", is highlighted
- The words "Car, Bicycle, Auto Aeroplane" audio is played and displayed in a picture in level 3. The odd one, "Aeroplane", is highlighted
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the words "Bicycle, Scooter, Auto, Banana" is played and displayed in a picture in level 1. The child must find the odd one. Suppose the child correctly finds the odd one as "Banana". In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response.
- The audio for the words "Apple, Watermelon, Grapes, Tomato" is played and displayed in a picture in level 2. The child has to find the odd one. Suppose the child correctly finds the odd one as "Tomato". In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response
- The audio for the words "Car, Bicycle, Auto Aeroplane" is played and displayed in a picture in level 3. The child must find the odd one. Suppose the child correctly finds the odd one as "Aeroplane". In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response.
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the words "Bicycle, Scooter, Auto, Banana" is played in level 1. The child must find the odd one. If the child correctly finds the odd one as "Banana", then a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response.
- The audio for the words "Apple, Watermelon, Grapes, Tomato" is played in level 2. The child has to find the odd one. If the child correctly finds the odd one as "Tomato", then a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response.
- The audio for the words "Car, Bicycle, Auto Aeroplane" is played in level 3. The child must find the odd one. If the child correctly finds the odd one as "Aeroplane", then a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response.
Here the child is introduced to the concept of the odd one out in auditory comprehension. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses. In the training session, there are levels according to the complexity of the task
To evaluate whether the child understands the concept of the odd one out in auditory comprehension, they undergo testing with a scoring system. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response
d. Stories :
The child has to listen to and understand the stories. Questions from the story will be asked at the end of the story. Closed-ended and open-ended questions will be asked. Closed-ended questions require answers by selecting from a limited number of options, such as multiple-choice questions. For example, in the App, the child is given three numbered boxes of 1, 2, and 3 as choices. The child has to answer with the options provided. Open-ended questions cannot be answered with a "yes" or "no" response but require a response in sentences or paragraphs. Stories include three levels. The levels increase in complexity from levels 1 to 3. Stories like "Thirsty Crow" and "Fox and Crow" with closed-ended questions are included in levels 1 and 2, respectively. Stories like "Monkey and crocodile" with closed and open-ended questions are in level 3.
- Instructions for Preview
- The storys audio is played, and pictures are displayed for levels 1, 2, and 3
- Instructions for Training
- Questions from the story are asked. Stories like "Thirsty Crow" and "Fox and Crow" with closed-ended questions are included in levels 1 and 2, respectively. Stories like "Monkey and crocodile" with closed and open-ended questions are in level 3. The child has to listen to the questions and answer the closed and open-ended questions. If the Child answers correctly, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response
- Instructions for Testing
- Questions from the story are asked. Stories like "Thirsty Crow" and "Fox and Crow" with closed-ended questions are included in levels 1 and 2, respectively. Stories like "Monkey and crocodile" with closed and open-ended questions are in level 3. The child must listen to and answer the closed and open-ended questions. If the child answers correctly, then a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response
Here the child is introduced to the concept of stories in auditory comprehension. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept.
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses. In the training session, there are levels according to the complexity of the task
To evaluate whether the child understands the concept of stories in auditory comprehension, they undergo testing with a scoring system. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
5. AUDITORY MEMORY AND SEQUENCING
(Remembering words in order)
Definition
Auditory memory is the ability to remember spoken utterances, and auditory sequencing is the ability to understand and recall the order of sounds, words, and sentences. Auditory memory involves taking in the information presented, processing it, storing it in one mind, and then recalling what one has heard. If a child struggles with auditory memory, they can find it challenging to follow instructions and pay attention. Auditory memory also plays a crucial role in literacy as it is one area of auditory processing that directly impacts reading, spelling, writing, and math skills. The child can be given a set of tasks to be completed. If the child meets all the tasks but not in order, then there is a possible issue in auditory sequencing. While the child performs the tasks in order but cannot recall all of them, auditory memory is a potential issue. The words or objects the child understands daily and registered in the brain. Repeated exposure leads to the storage of particular words. They then associate it with a specific meaning and store it in their memory.
Task
The parents have to expose the child to the sentences in the App. The child has to listen, memorize the audio message, and recall and identify the message. Auditory memory and sequencing or Remembering words in order - Category 6 in the App has three categories. It includes memorizing keywords in the sentence, auditory memory: item selection, and memory of events.
a.Memorizing keywords in the sentence :
The child must listen to and remember the keywords in the sentence. It has three levels. The levels increase in complexity from levels 1 to 3
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the sentence "Balu got a ball and bat" is played, and the two keywords" ball and bat" are displayed in a picture in level 1.
- The sentence "He got mangoes, guava, and papaya from his garden" audio is played, and the three keywords" mangoes, guava and papaya" are displayed in a picture in level 2.
- The audio "Arjun had toys of car, aeroplane, bicycle, and train" is played. The four keywords" car, aeroplane, bicycle, and train" are displayed in a picture in level 3.
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the sentence "Balu got a ball and bat" is played, and the two keywords "ball and bat" are displayed in a picture in level 1. The child must listen, memorize, and repeat the keywords "ball and bat"—two choices are "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete response.
- The audio for the sentence "He got mangoes, guava and papaya from his garden" is played, and the three keywords" mangoes, guava and papaya" are displayed in a picture in level 2. The child has to listen and memorize and repeat the keywords" mangoes, guava, and papaya"—two choices are "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete response.
- The audio for the sentence "Arjun had toys of car, aeroplane, bicycle, and train" is played. The four keywords" car, aeroplane, bicycle, and train" are displayed in a picture in level 3. The child must listen, memorize, and repeat the keywords "car, aeroplane, bicycle, and train"—two choices are "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete response.
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the sentence "Balu got a ball and bat" is played in level 1. The child must listen, memorize, and repeat the keywords "ball and bat"—two choices are "Completed" and "Not completed. Suppose the child completes this task correctly by repeating the two keywords. In that case, a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect or incomplete response.
- The audio for the sentence "He got mangoes, guava and papaya from his garden" is played in level 2. The child must listen, memorize, and repeat the keywords mangoes, guava, and papaya"—two choices given as "Completed" and "Not completed. Suppose the child completes this task correctly by repeating the three keywords. In that case, a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect or incomplete response.
- The audio for the sentence "Arjun had toys of car, aeroplane, bicycle, and train" is played in level 3. The child must listen and memorize and repeat the keywords "car, aeroplane, bicycle, and train"—two choices are "Completed" and "Not completed. Suppose the child completes this task correctly by repeating the four keywords. In that case, a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect or incomplete response.
Here the child is introduced to the concept of memorizing keywords in a sentence in auditory memory and sequencing. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept.
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses. In the training session, there are levels according to the number of keywords provided.
To evaluate whether the child understands the concept of memorizing keywords in a sentence in auditory memory and sequencing, they undergo testing with a scoring system. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer.
b.Auditory memory: item selection :
The parents have to expose the child to the words in the App. The child has to listen, memorize and select the words among the other options given. Once your child can choose one word in the item selection, move on to the auditory memory of two words. Gradually increase the number in the options set as your childs auditory memory develops.
a) Noun + Noun :
The child has to listen to the phrase or sentence, memorize and find the nouns in the phrase or sentence.
- Instructions for Preview
- The nouns "Auto and Bicycle" audio is played and displayed in a picture. The first noun is "Auto", and the second is "Bicycle".
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the nouns "Auto and Bicycle" is played and displayed in a picture with other pictures. The child must listen, memorize, and find the nouns "Auto and bicycle" played among the other images. Suppose the child completes this task correctly by finding all the nouns. In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete response
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the nouns "Auto and Bicycle" is played and displayed in a picture with other pictures. The child must listen, memorize, and find the nouns "Auto and bicycle" played among the other images. If the child completes this task correctly by finding all nouns, then a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect or incomplete response
Here the child is introduced to the concept of item selection of nouns in auditory memory and sequencing. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of item selection of nouns in auditory memory and sequencing. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
b) Adjective + Noun :
The child has to listen to the phrase or sentence, memorize and find the adjective, followed by the noun in the phrase or sentence
- Instructions for Preview
- The noun "Give me the small pencil" audio is played, and the adjective and noun "small pencil" is displayed in a picture. The adjective is "small", and the noun is "pencil".
- Instructions for Training
- The adjective and noun "Give me the small pencil" audio is played and displayed in a picture with other pictures. The child must listen, memorize and find the adjective and noun "small pencil" played among the other pictures. Suppose the child completes this task correctly by finding the adjective and nouns. In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response
- Instructions for Testing
- The adjective and noun "Give me the small pencil" audio is played and displayed in a picture with other pictures. The child must listen, memorize and find the adjective and noun "small pencil" played among the other pictures. If the child completes this task correctly by finding all the nouns, a score of 1 is given. A score of 0 is for the incorrect response
Here the child is introduced to the concept of item selection of "adjective" and "noun" in auditory memory and sequencing. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of item selection of "adjective" and "noun" in auditory memory and sequencing. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
c) Noun + Verb :
The child has to listen to the phrase or sentence, memorize and find the noun and verb in the phrase or sentence
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the noun+verb "Children are playing" is played and displayed in a picture. The noun is "Children", and the verb is "playing",
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the noun+verb "Children are playing" is played and displayed in a picture with other pictures. The child must listen and memorize and find the noun+verb "Children are playing" that is played among the other images. Suppose the child completes this task correctly by finding the noun+verb. In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete response
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the noun+ verb "Children are playing" is played and displayed in a picture with other pictures. The child must listen and memorize and find the noun+verb "Children are playing" that is played among the other images. If the child completes this task correctly by finding all the nouns, then a score of 1 is given. A score of 0 is given for the incorrect or incomplete response
Here the child is introduced to the concept of item selection of noun+verb in auditory memory and sequencing. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of item selection of noun+verb in auditory memory and sequencing. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
d) Noun + preposition+ noun :
The child has to listen to the phrase or sentence, memorize and find the Noun, preposition, and Noun in the phrase or sentence
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the noun + preposition+ noun "The fruits are on the table" is played and displayed in a picture. The first noun is "Fruits", the preposition is "on", and the second noun is "table".
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the noun + preposition+ noun "The fruits are on the table" is played and displayed in a picture with other pictures. The child has to listen and memorize and find the noun + preposition+ noun "The fruits are on the table" played among the other images. Suppose the child completes this task correctly by finding the noun + preposition+ noun. In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete response
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the noun + preposition+ noun "The fruits are on the table" is played and displayed in a picture with other pictures. The child must listen, memorize, and find the noun + preposition+ noun "The fruits are on the table" played among the other images. If the child completes this task correctly by finding the noun + preposition+ noun, then a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is given for the incorrect or incomplete response
Here the child is introduced to the concept of item selection of noun + preposition+ noun in auditory memory and sequencing. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of item selection of noun + preposition+ noun in auditory memory and sequencing. A score of 1 is given for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
c. Memory of Events :
The parents must expose the child to the sentences or events in the App. The child has to listen, memorize and repeat the sentences or events. Initially, the child can repeat the sentence or event without sequence; later, they must repeat the sentence or event with sequence. For example, the parent says, "Meena visited a zoo. She saw many animals in the zoo. She loves animals. If the child repeats it as "She loves animals. She saw many animals in the zoo. Meena visited a zoo" means that the auditory memory is present, and sequencing needs to be worked on so that the child repeats it in the same order as "Meena visited a zoo. She saw many animals in the zoo. She loves animals.’
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the event "Ajay cook’s food. He made a sandwich. He shared it with his friends. Everyone liked the sandwich" is played, and the event is in a picture
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the event "Ajay cook’s food. He made a sandwich. He shared it with his friends. Everyone liked the sandwich" is played, and the event is displayed in a picture. The child must listen, memorize and repeat the event that is played. Suppose the child completes this task correctly by repeating the event. In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect or incomplete response
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the event "Ajay cooks food. He made a sandwich. He shared it with his friends. Everyone liked the sandwich" is played. The child must listen, memorize and repeat the played event—two choices are "Completed" and "Not completed. If the child completes this task correctly by repeating the event, then a score of 1 is given. A score of 0 is for the incorrect response.
Here the child is introduced to the concept of memory of events in auditory memory and sequencing. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept.
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of memory of events in auditory memory and sequencing. A score of 1 is given for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer.
6. AUDITORY COGNITION
(Understanding complex speech)
Definition
Auditory cognition describes a group of processes by which the brain makes sense of the sound world. It is the ability to infer and process higher-order thinking concepts. It includes the intellectual power to reason, question, predict and infer. Auditory cognition also involves attention, memory, and emotional responses. For example, when the parent says it is raining outside, they should be able to think and understand that they should carry an umbrella while going out.
Task
The parents have to expose the child to the questions in the App. The child has to listen, understand, reason, and logically answer the question. It has four categories. Auditory cognition or Understanding complex speech - Category 7 in the App includes Problem-solving, Cause, and Effect, Guess Who, and Reasoning.
a. Problem-Solving :
Parents have to expose their children to the questions in the App. The question consists of a problem that requires a solution as an answer. The child has to listen, understand and think about a solution for the problem and answer it by choosing the correct answer among the three other options given
Question: What to do when it rains?
- We use an umbrella
- We use a cloth to cover our head
- We use our hands to cover our head
Answer: We use an umbrella
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the following question is played, and the answer is in a picture
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the following question with a problem will be played. The options are played and displayed in a picture. The child must listen, understand and think about a solution for the problem and answer it by choosing the correct answer among the three other options given. Suppose the child completes this task by providing the correct answer. In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response
- We use an umbrella
- We use a cloth to cover our head
- We use our hands to cover our head
- Instructions for Testing
- They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of problem-solving in auditory cognition. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
- We use an umbrella
- We use a cloth to cover our head
- We use our hands to cover our head
Here the child is introduced to the concept of problem-solving in auditory cognition. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Question: What to do when it rains?
Answer: We use an umbrella
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
Question: What to do when it rains?
Answer: We use an umbrella
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of problem-solving in auditory cognition. A score of 1 is for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
Question: What to do when it rains?
Answer: We use an umbrella
b. Cause and effect :
i. Level 1 :
The parents must expose the child to a sentence or a statement in the App. The sentence consists of a cause and effect. The child has to understand the statement and find the cause and effect.
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the following statement is played. The answer, which has cause and effect, is played and displayed in a picture
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the following statement is played, and the options are played and displayed in a picture. The child must understand the statement and find the cause and effect. If the child completes this task by finding the cause and effect, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the following statement is played, and the options are played and displayed in a picture. The child must understand the statement and find the cause and effect. If the child completes this task by finding the cause and effect, then a score of 1 is given. A score of 0 is for the incorrect response
Here the child is introduced to the concept of cause and effect (level 1) in auditory cognition. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Statement: She dropped the glass, and the glass broke
Answer:
Cause: She dropped
Effect: Glass broke
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
Statement: She dropped the glass, and the glass broke
Answer:
Cause: She dropped
Effect: Glass broke
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of cause and effect (level 1) in auditory cognition. A score of 1 is given for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
Statement: She dropped the glass, and the glass broke
Answer:
Cause: She dropped
Effect: Glass broke
b. Cause and effect :
ii. Level 2 :
The parents have to expose the child to a phrase or sentence about an event in the App. The event consists of the effect. The child has to understand the event and find the cause among the options given
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the following sentence consists of the event. The answer, which has the "cause", is played and displayed in a picture
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the following sentence consists of the event. The options are played and displayed in a picture. The child must listen, understand and understand it and find the cause, which is the correct answer among the three other options. Suppose the child completes this task by providing the correct answer. In that case, a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response
- As it was raining
- As it was sunny
- As it was spring
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the following sentence consists of the event. The options are played and displayed in a picture. The child must listen, understand and understand it and find the cause, which is the correct answer among the three other options. If the child completes this task by providing the correct answer, then a score of 1 is given, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect response.
- As it was raining
- As it was sunny
- As it was spring
Here the child is introduced to the concept of cause and effect (level 2) in auditory cognition. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Event: The Street became muddy
Answer: As it was raining
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
Event: The Street became muddy
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of cause and effect (level 2) in auditory cognition. A score of 1 is given for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
Event: The Street became muddy
c. Guess who :
The parents have to expose the child to phrases or sentences about an event in the App. The event consists of clues to the answer. The child has to understand the event and guess the correct answer among the options given. For example, the parent says the following phrases or sentences to the child. The child has to understand the clues and guess the correct answer.
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the following sentence consisting of clues is played. The answer is played and displayed in a picture
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the following sentence consists of clues, and the options are played and displayed in a picture. The child must understand the clues and guess the correct answer among the options given. If the child completes this task by guessing the correct answer, then a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response Clues: It’s an animal. Gives us milk. Eats mainly grass
- Cow
- Dog
- Lion
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the following sentence consists of clues, and the options are played and displayed in a picture. The child must understand the clues and guess the correct answer among the options given. If the child completes this task by guessing the correct answer, then a score of 1 is given. A score of 0 is given for the incorrect response Clues: It’s an animal. Gives us milk. Eats mainly grass
- Cow
- Dog
- Lion
Here the child is introduced to the concept of guess who in auditory cognition. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept
Clues: It’s an animal. Gives us milk. Eats mainly grass
Answer: Cow
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
To evaluate whether the child understands the concept of guess who in auditory cognition, they undergo testing with a scoring system. A score of 1 is given for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer.
d. Reasoning :
The parents have to expose the child to the questions in the App. The question consists of an event and requires Reasoning as an answer. The child has to understand and think about the reason for the event and answer it by choosing the correct answer among the three other options given
- Instructions for Preview
- The audio for the following question is played. The answer, which consists of the reason, is played and displayed in a picture
- Instructions for Training
- The audio for the following question is played. The answer consists of the reason, and the options are played and displayed in a picture. The child must understand the question, reason it out and provide the correct answer among the options given. If the child completes this task by guessing the correct answer, then a thumbs-up symbol is displayed, and a thumbs-down symbol is for the incorrect response Question: Why do we go to school?
- To eat
- To study
- To play
- Instructions for Testing
- The audio for the following question is played. The answer consists of the reason, and the options are played and displayed in a picture. The child has to understand the question, reason it out and provide the correct answer among the options given. If the child completes this task by guessing the correct answer, then a score of 1 is given. A score of 0 is for the incorrect response Question: Why do we go to school?
- To eat
- To study
- To play
Here the child is introduced to the concept of Reasoning in auditory cognition. A few examples show the child how to perform the task and help the child learn the concept.
Question: Why do we go to school?
Answer: To study.
Here the child is given practice with the learned concept and gets feedback for correct and incorrect responses
They undergo testing with a scoring system to evaluate whether the child understands the concept of Reasoning in auditory cognition. A score of 1 is given for the correct response, and a score of 0 is for the incorrect answer
 COCHILA
COCHILA